Research Projects
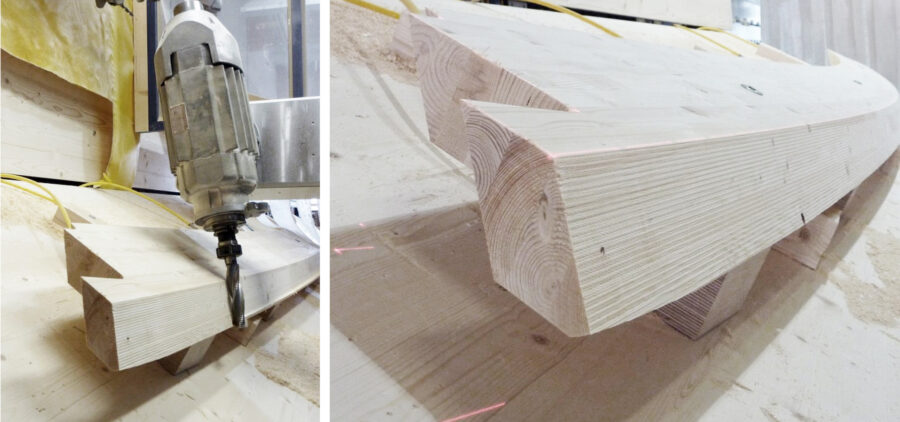
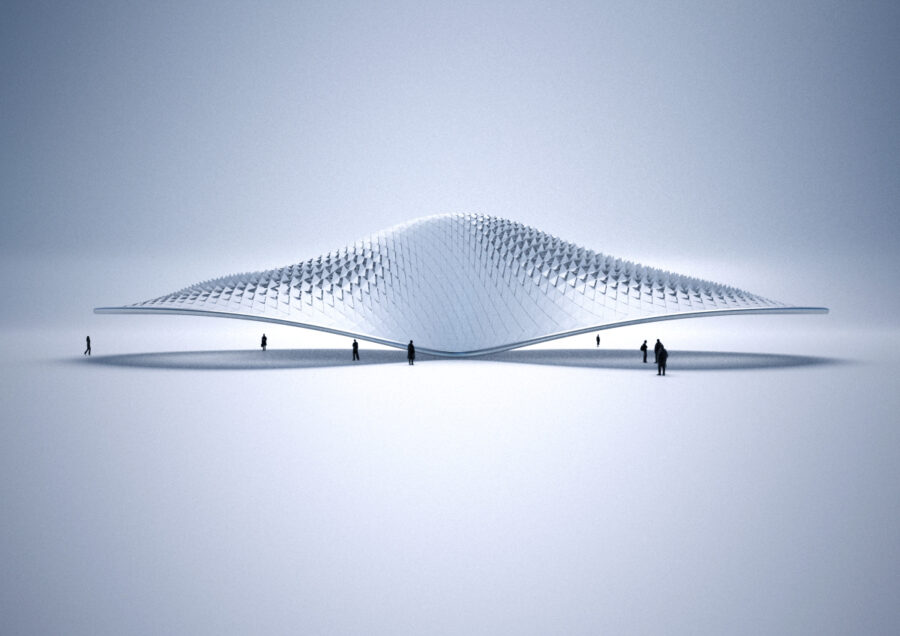
CategoryESR14- DESIGN FOR ASSEMBLY
Industrial Partners: designtoproduction, Bluhmer Lehmann. One of the central achievements of digital chain is the ability to mass customise building elements creating individualised solutions and enabling new kinds of building geometries. While methods for the design and production of customised elements have matured, the planning of assembly procedures remains undeveloped in the building sector – in contrast to for example to product design .
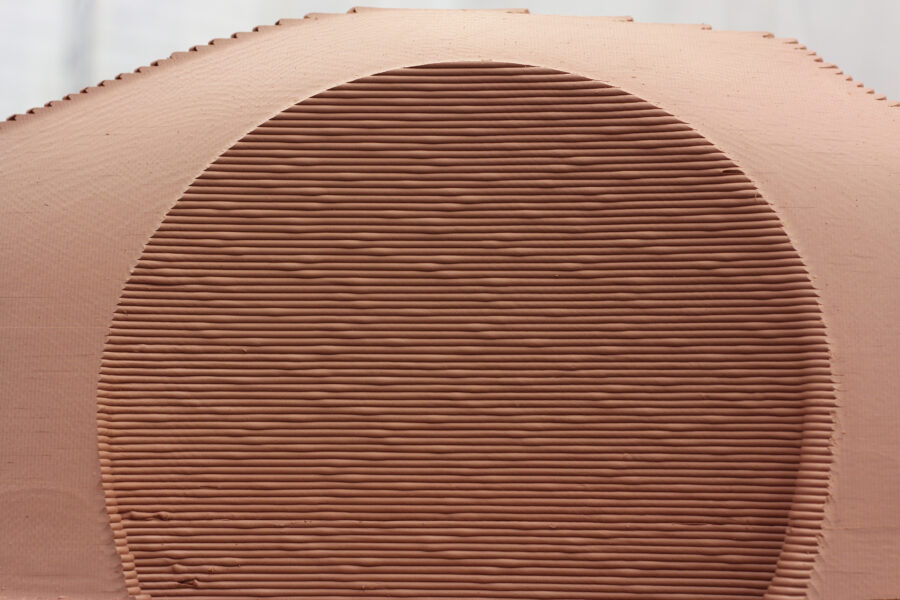
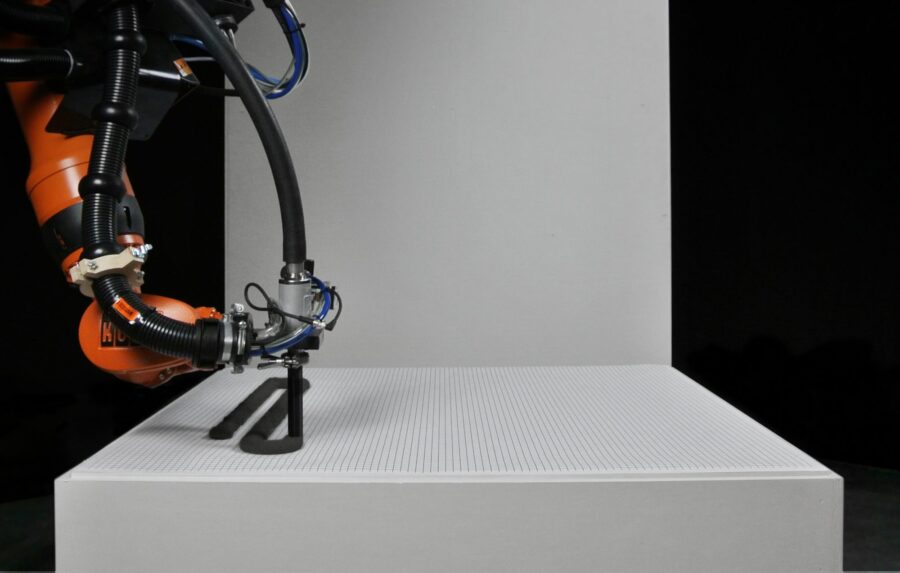
ESR13- APPLIED ROBOTICS – CONTROLLED MATERIAL DEPOSITION
Industrial modelling clay plays an important role in automotive design when modelling ‘class-A’ surfaces. Design studios around the world use it to prototype vehicles at a 1:1 scale, combining several technologies: sculpting, CAD freeform surface modelling, 3D scanning and CNC machining. This research investigates the use of this material for additive manufacturing.
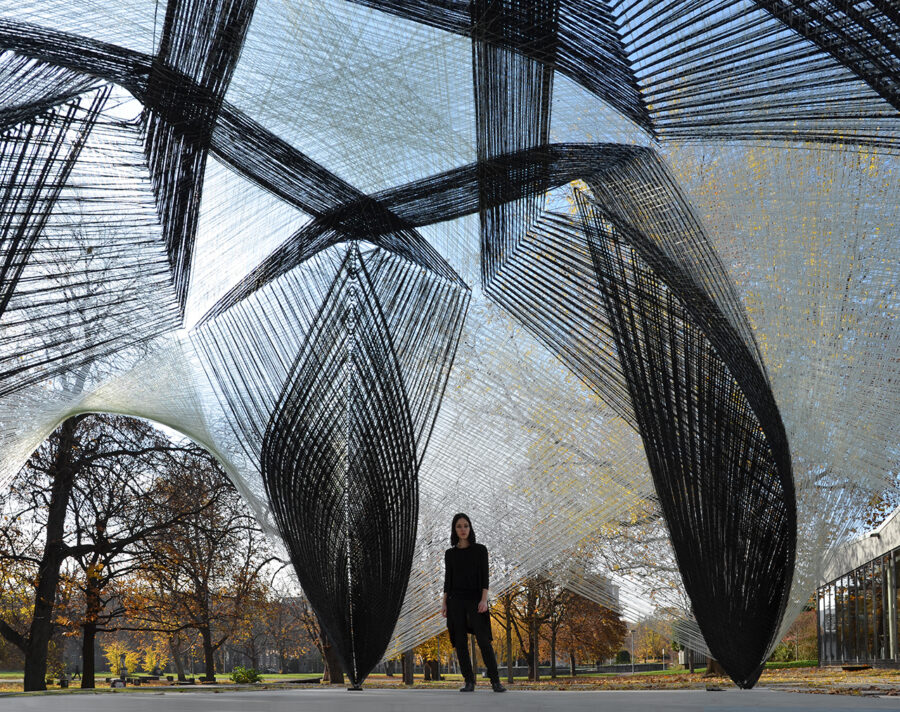
ESR12- MATERIAL GRADIENT FRP
Current practices emphasise the stiffness of material to ensure structural performance. Building systems such as louvers or other adjustable shading systems and employ mechanical means to activate change.
ESR11- Concrete Deposition
Generally, applied digital fabrication technologies are subtractive causing material waste at fabrication level. New research explores additive processes in building realization creating more sustainable and materially smart solutions.
ESR09- SIMULATING CONCRETE FORMWORK
The PhD student will investigate and develop methods for the simulation of formwork in architecture. This will entail research into the transformation between states of fluidity and solidity germane to casting, the dynamic relationship between casting material, formwork and environmental factors, and the architectural possibilities and consequences.
ESR08- VIRTUAL PROTOTYPING FRP
Current practice uses digital fabrication technologies to optimise standardised fabrication processes. Often accompanied by trial-and-error approaches, the limits of digital fabrication methods are quickly reached without a thorough understanding of the strength and limits of the forming processes and the materials.