A COMPARATIVE OVERVIEW OF GENERATIVE APPROACHES FOR COMPUTATIONAL FORM-FINDING OF BENDING-ACTIVE TENSILE STRUCTURES
ESR01- MULTIPLE STATES OF EQUILIBRIUM FOR BENDING-ACTIVE (TENSILE) STRUCTURES
AUTHOR: EVY L. M. SLABBINCK
Images by Seiichi Suzuki
Publication: A comparative overview of generative approaches for computational form-finding of bending-active tensile structures. In: Proceedings of the IASS Annual Symposium 2017, 25-28 Sept. 2017, Hamburg, Germany by Suzuki, S.; Slabbinck, E. L. M.; Knippers, J.
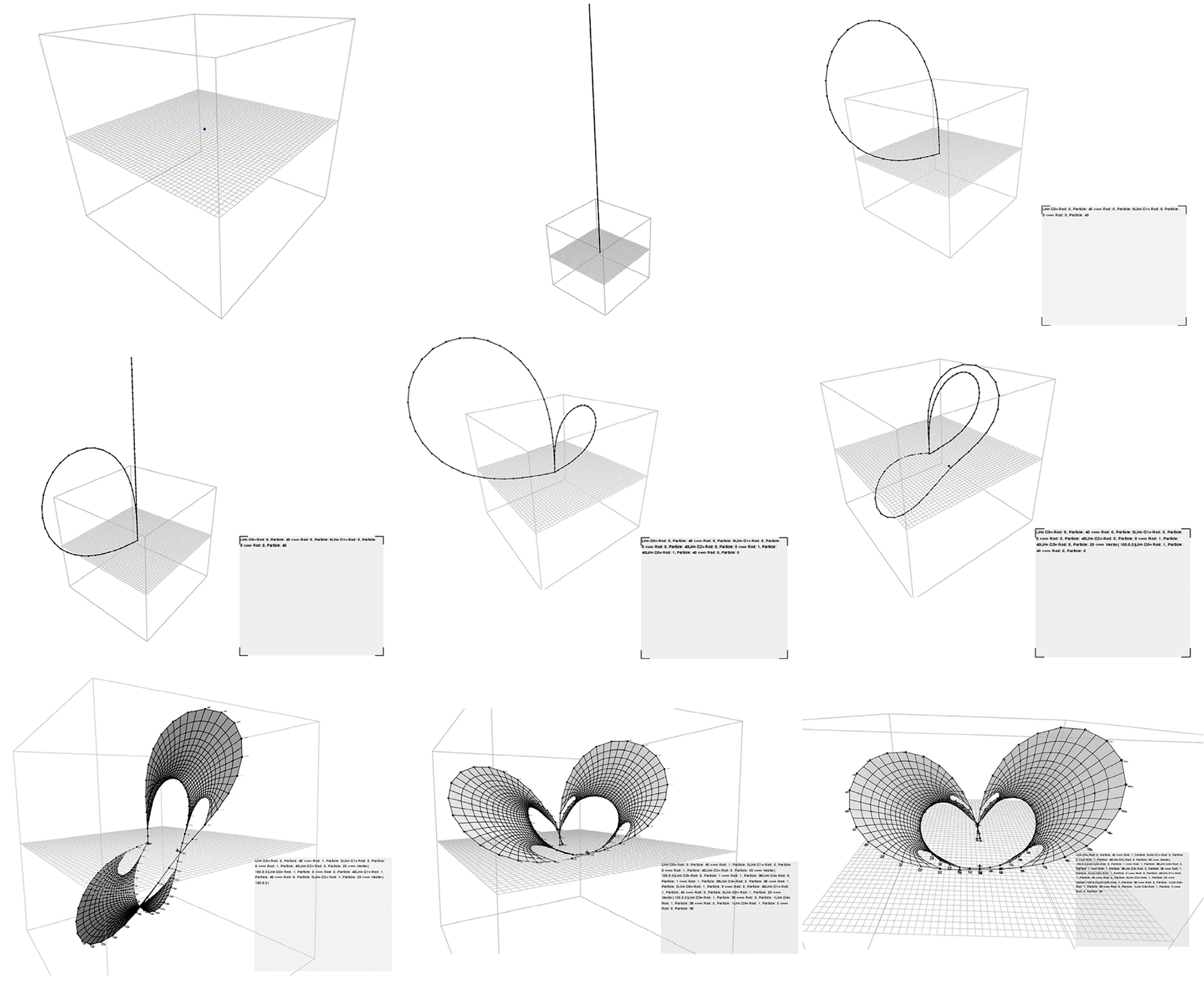
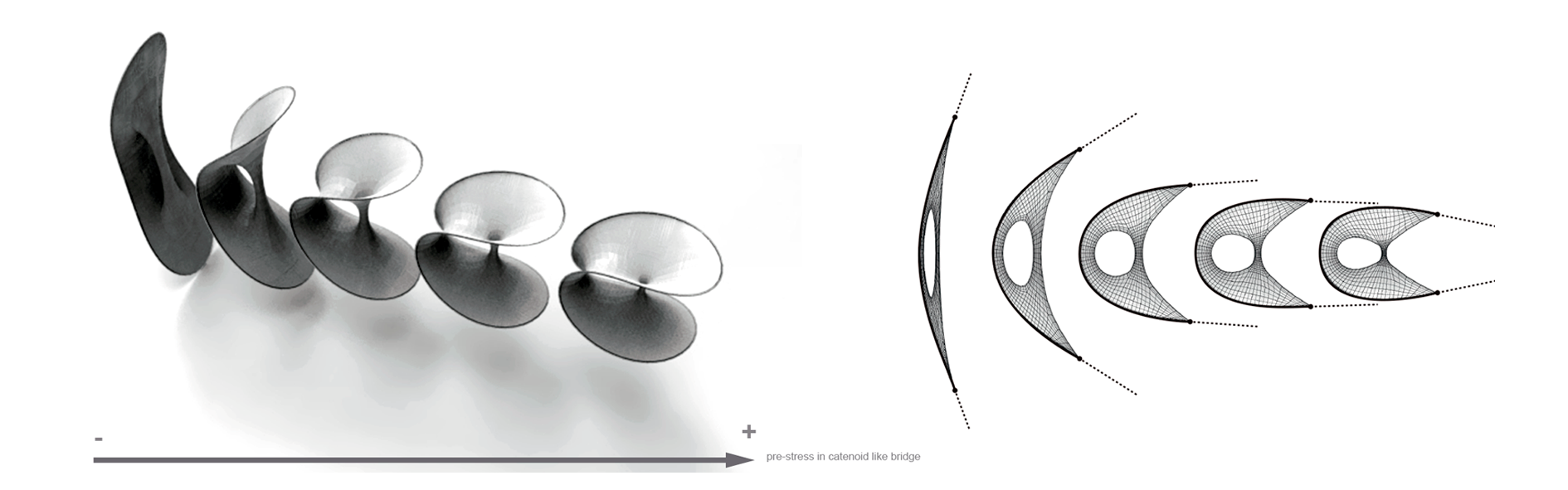
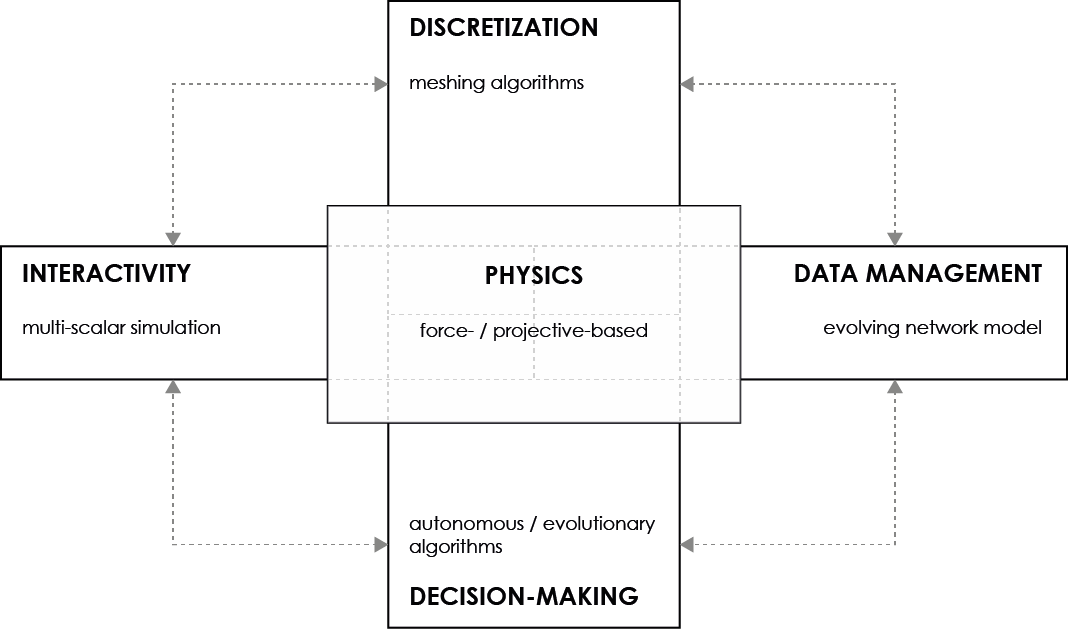
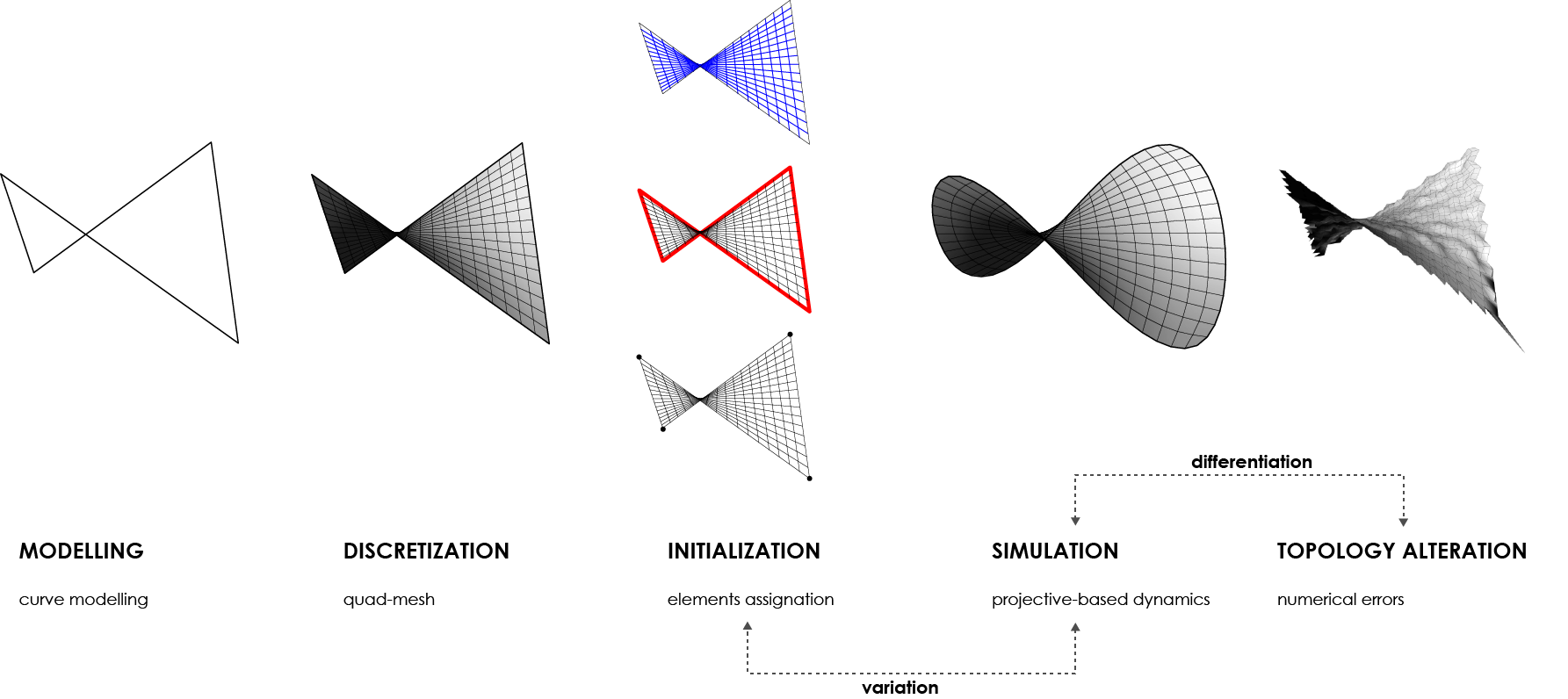
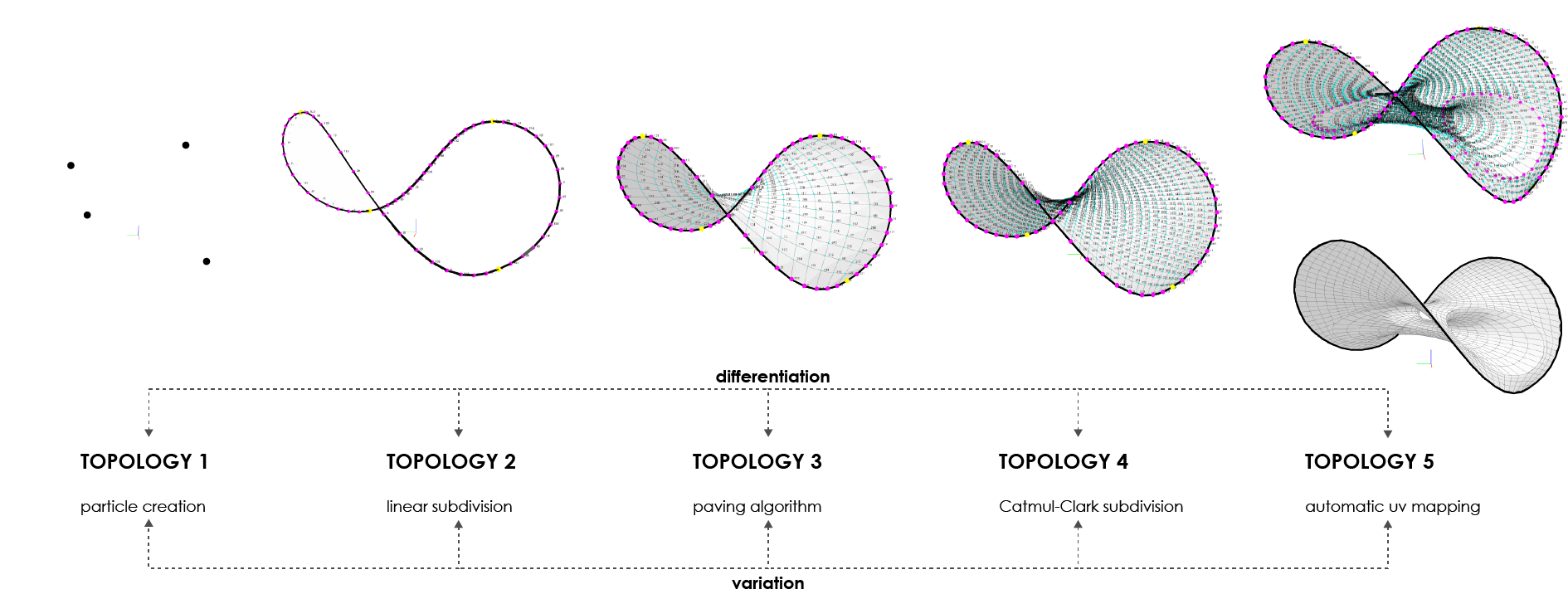
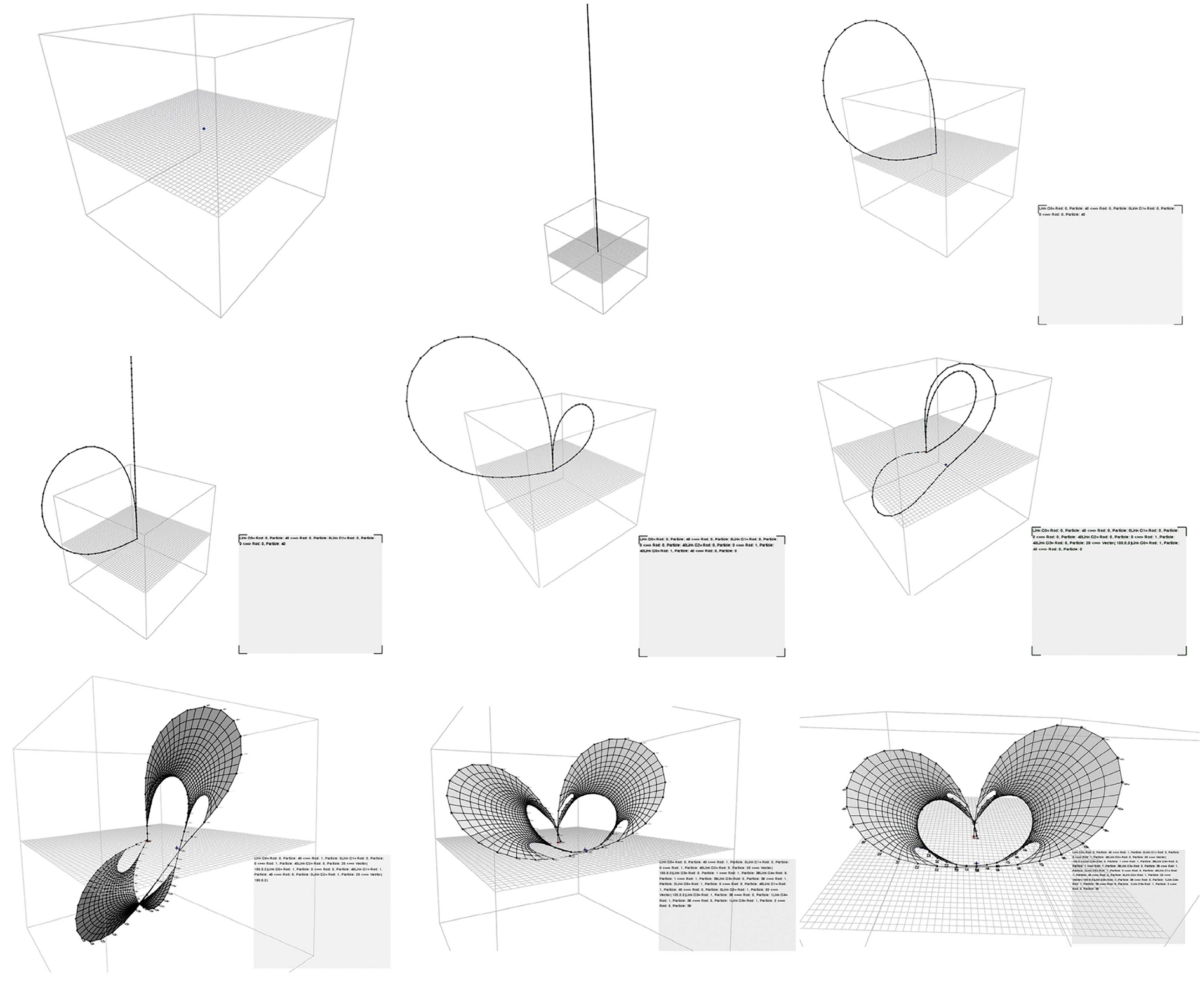
Bending-active tensile hybrid structures refers to the coupling of bending- and tension-form-active components within a unique and stiffer construct. The variety of possible shapes applicable to the design of these structures demands new ideas around real-time physics-based simulations for the development of more flexible and interactive design spaces. This paper seeks to contribute to this research by identifying and comparing two main families of generative approaches for form-finding: geometric-driven and topology-driven. Fundamental differences of both approaches lie in the management and activation of parameters while the algorithm is running. As geometric-driven, variations in form-found geometries are regulated through dynamic alterations of metric parameters without affecting initial topological conditions. On the other hand, topology-driven approaches extend the latter by enabling differentiation through interactive adjustments of topological models. In this paper, the core ideas of geometric- and topology-driven approaches are identified and discussed. Alongside to this, the presented study serves to strategically analyze advantages and disadvantages of both approaches, and the influence that dynamic topological models has when pursuing a desirable solution.